Flexible printed circuit boards are a bendable type of circuit board manufactured for several reasons. Its benefits over traditional circuit boards include decreasing assembly errors, being more resilient in harsh environments, and being capable of handling more complex electronic configurations. These circuit boards are made using electrolytic copper foil, a material that is rapidly proving to be one of the most important in the electronics and communication industries.
How Flex Circuits Are Made
Flex Circuits are used in electronics for a variety of reasons. As said earlier, it decreases assembly errors, is more environment-resilient, and can handle complex electronics. However, it can also decrease labor costs, reduce weight and space requirements, and lessens interconnection points which increase stability. For all these reasons, flex circuits are one of the most in-demand electronic parts in the industry.
A flexible printed circuit is composed of three main components: Conductors, Adhesives, and Insulators. Depending on the structure of the flex circuits, these three materials are arranged for current to flow in the customer’s desired way, and for it to interact with other electronic components. The most common material for the flex circuit’s adhesive are epoxy, acrylic, PSAs, or sometimes none, while commonly-used insulators include polyester and polyamide. For now, we are most interested in the conductors used in these circuits.
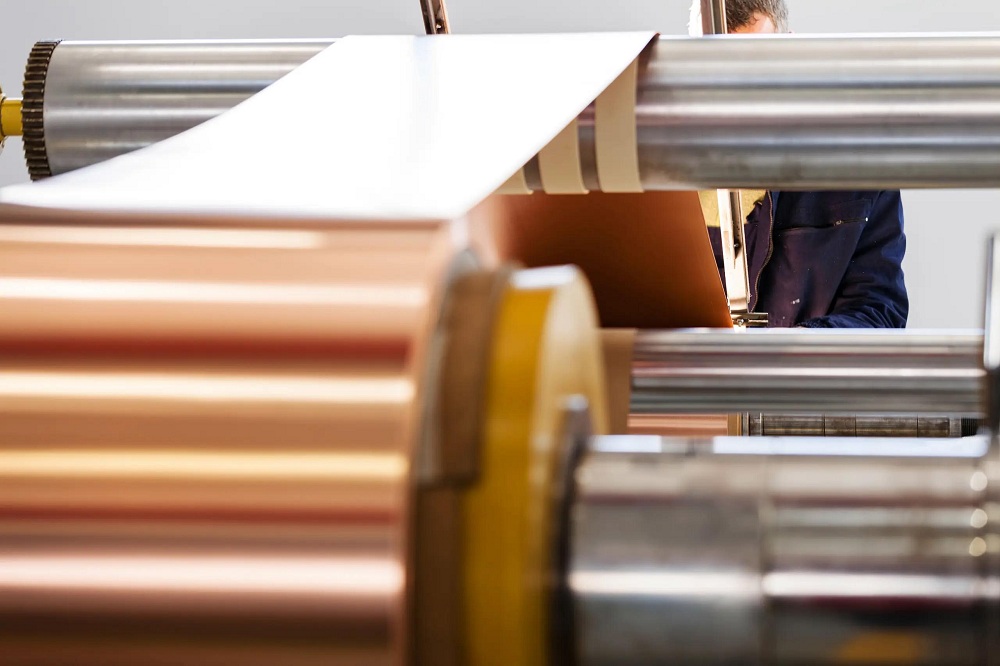
While other materials such as silver, carbon, and aluminum can be used, the most common material used for conductors is copper. Copper foil is considered an essential material for the manufacturing of flex circuits, and it is produced in two ways: rolling annealing or electrolysis.
How Copper Foils Are Made
Rolled annealed copper foil is produced through rolling heated sheets of copper, thinning them down and creating a smooth copper surface. The copper sheets are subjected to high temperatures and pressures through this method, producing a smooth surface and improving ductility, bendability, and conductivity.
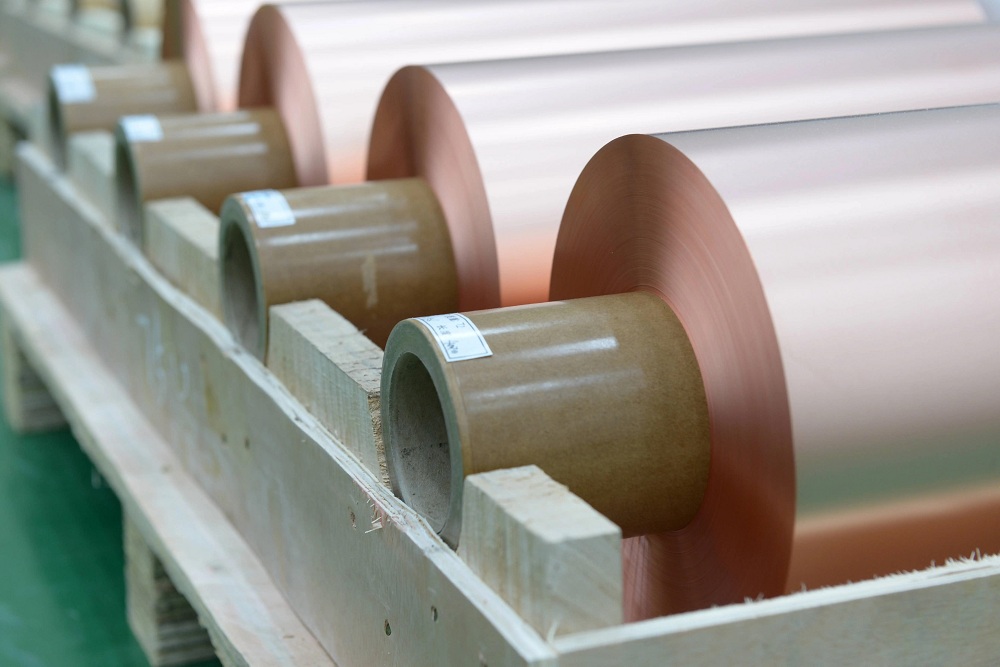
Meanwhile, electrolytic copper foil is produced by using the electrolysis process. A copper solution is created with sulfuric acid (with other additives depending on the manufacturer’s specifications). An electrolytic cell is then run through the solution, which then causes copper ions to precipitate and land on the cathode surface. Additives may also be added to the solution which can alter its internal properties as well as its appearance.
This electroplating process continues until the cathode drum is removed from the solution. The drum also controls how thick the copper foil is going to be, as a faster-rotating drum also attracts more precipitate, thickening the foil.
Regardless of the method, all copper foils produced from both of these methods will still be treated with bonding treatment, heat resistance treatment, and stability (anti-oxidation) treatment after. These treatments enable the copper foils to be able to bind better to the adhesive, be more resilient to the heat involved in the creation of the actual flexible printed circuit, and prevent oxidation of the copper foil.
Rolled Annealed vs Electrolytic
Because the process for creating a copper foil of rolled annealed and electrolytic copper foil is different, they also have different advantages and disadvantages.
The main difference between the two copper foils is in terms of their structure. A rolled annealed copper foil will have a horizontal structure at normal temperature, which then morphs into a lamellar crystal structure when subject to high pressure and temperature. Meanwhile, electrolytic copper foil retains its columnar structure at both normal temperatures and high pressures and temperatures.
This creates differences in the conductivity, ductility, bendability, and cost of both types of copper foil. Because rolled annealed copper foils are generally smoother, they are more conductive and are more appropriate for small wires. They are also more ductile and are generally more bendable than electrolytic copper foil.
However, the simplicity of the electrolysis method ensures that electrolytic copper foil has a lower cost than rolled annealed copper foils. Take note though, that they might be a suboptimal option for small lines, and that they have a worse bending resistance than rolled annealed copper foils.
In conclusion, electrolytic copper foils are a good low-cost option as conductors in a flexible printed circuit. Because of the flex circuit’s importance in electronics and other industries, it, in turn, makes electrolytic copper foils an important material as well.
Post time: Sep-14-2022